Epidemiology, Market Landscape, and Innovation Trends in Drug Development
About GCP ClinPlus
GCP ClinPlus is a leading China-based contract research organization (CRO) with 22 years of experience, over 500 global clients, and participation in more than 120 multinational clinical trials (MRCTs). We bring strong expertise in liver disease, having conducted over 50 liver disease studies, including 27 hepatitis B programs and 10 NDA submissions—4 of which were for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Our liver trials span biologics, RNA therapies, gene therapies, and small molecules.
Backed by a dedicated in-house medical team and a nationwide hospital/PI network, we ensure scientific rigor, efficient patient recruitment, and globally compliant data delivery. Our mission is to accelerate access to innovative liver disease therapies—especially in high-need markets like China.
Ⅰ. Epidemiology
1.1 Understanding Hepatitis B and Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is a malignant tumor that originates from liver cells, primarily presenting as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). HCC is by far the most common type, accounting for 80%–90% of all liver cancer cases. The disease is closely linked with chronic liver conditions such as hepatitis B and C infections, excessive long-term alcohol consumption, and fatty liver disease, contributing to a high incidence and mortality rate globally.
According to the China Primary Liver Cancer Clinical Registry Survey (2022), 77% of liver cancer cases in China are attributed to chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Among those infected with HBV, 3–5% progress to cirrhosis annually, and 5–10% of cirrhotic patients subsequently develop liver cancer each year.
1.2 Incidence and Mortality
China carries one of the world’s heaviest burdens of hepatitis B. As of 2022, the country recorded 367,000 new liver cancer cases and over 310,000 related deaths. While significant progress has been made in prevention through vaccination, early screening, and antiviral treatments, the five-year survival rate remains below 15%, largely due to late-stage diagnosis.
According to the 2022 Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B, China has approximately 86 million HBV carriers, with 20 to 30 million diagnosed as chronic hepatitis B patients. Although incidence has declined over the past decade, hepatitis B remains a serious public health issue, especially in rural areas and among high-risk populations.
Table1 Hepatitis B Incidence Rate by Year in China (2009-2020)
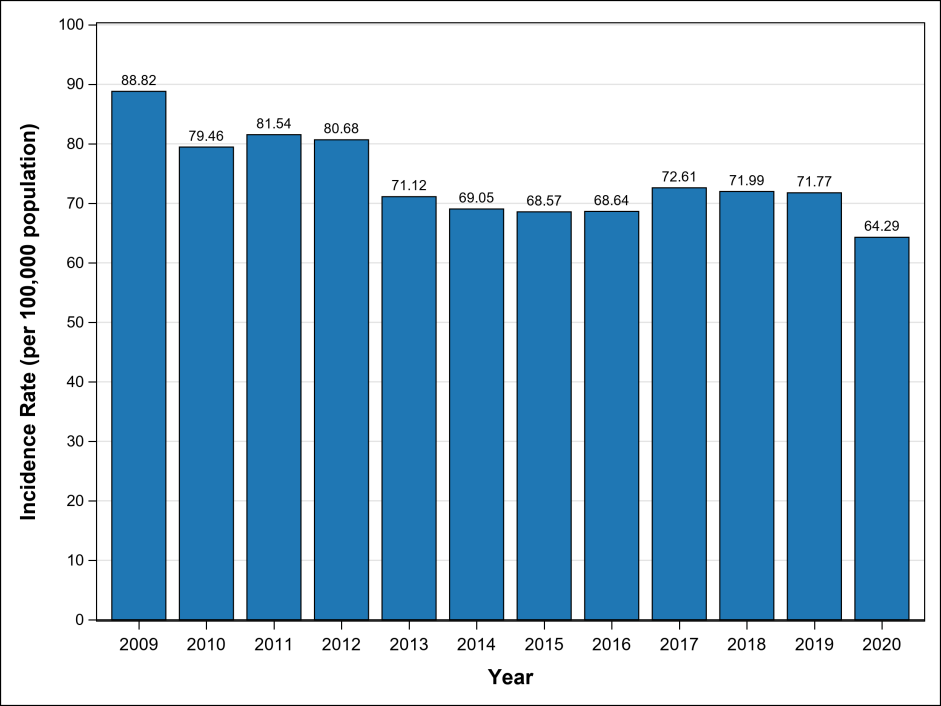
Table2 Incidence statistics of major cancer types (Unit: per 100,000)
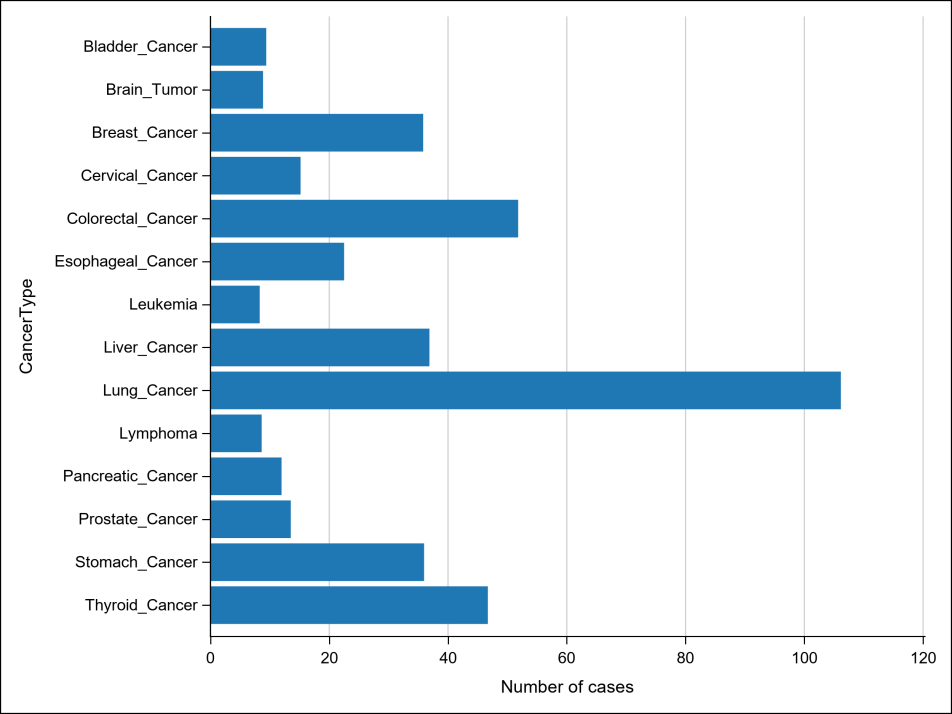
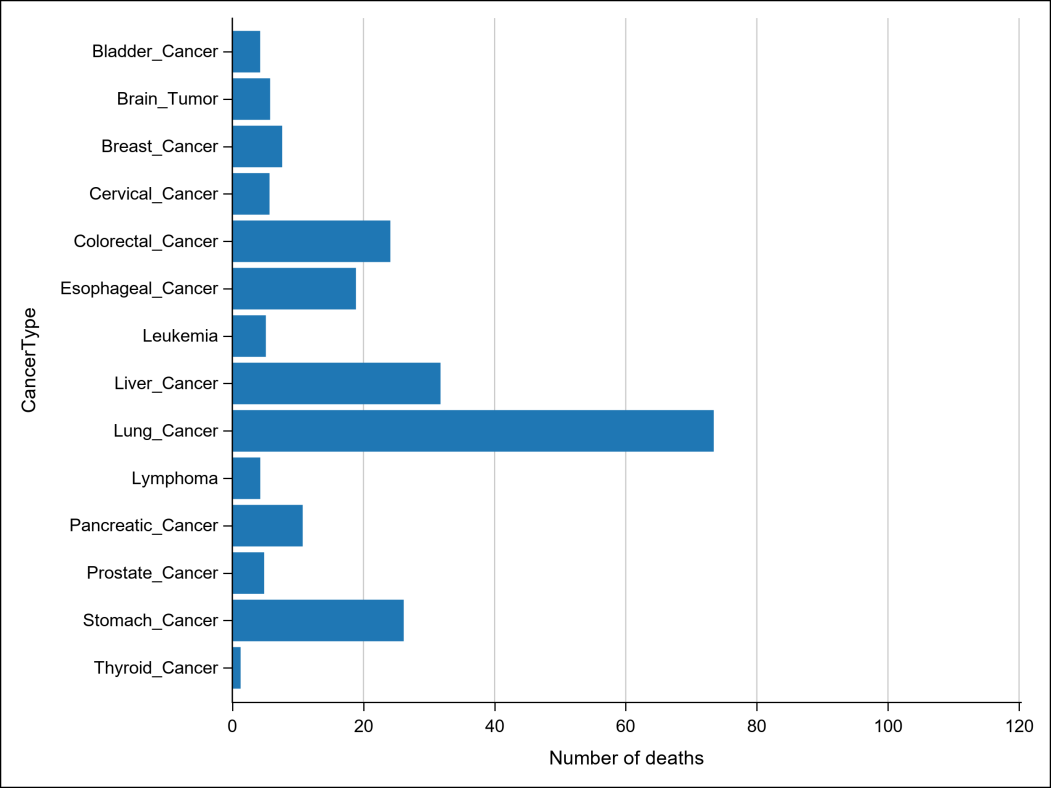
Table3 Death statistics of major cancer types (Unit: per 100,000)
Ⅱ. Hepatitis B Drug Market Analysis
2.1 Introduction to Globally Marketed Hepatitis B Therapeutics
Globally, the first-generation hepatitis B treatments were mainly interferons and nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs). To date, 12 hepatitis B drugs have been approved worldwide, with 11 of them available in China and included in the National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL). Notably, Jiangsu Hansoh’s Hengmu® (TMF) is a Class 1 innovative drug, while Pegboda® (pegbinterferon alfa-2b) is China’s first domestically developed long-acting interferon.
The majority of marketed hepatitis B drugs in China face fierce competition due to widespread generics and incremental innovations. Entecavir (ETV) and Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (TDF) remain the most widely used therapies.
2.2 Market Performance of Interferon-Based Hepatitis B Therapies
Interferons, which act by enhancing the body’s immune response, have played a foundational role in hepatitis B treatment. Long-acting pegylated interferons, including Pegasys® (Roche), PegIntron® (Merck), and Pegboda® (Amoytop), have been approved in China. However, international products have gradually withdrawn from the Chinese market due to declining sales and side effects.
Pegboda®, benefiting from local support and higher sales efforts, continues to grow in usage—especially in combination with NAs and as a preferred treatment in pediatric HBV cases. Its potential for synergy has positioned it as a viable component in future combination therapies.
2.3 Market Performance of Nucleos(t)ide Analogues (NAs)
• Entecavir (ETV): Since its 2005 launch in China, ETV enjoyed strong uptake until the implementation of national volume-based procurement (2018–2019), which significantly reduced prices and sales volumes. By 2023, ETV’s hospital sales had declined to approximately 1.5 billion RMB, with Bristol Myers Squibb maintaining the majority market share.
• Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (TDF): After peaking at 1.7 billion RMB in sales, TDF experienced a steep drop post-2019 due to price reductions from centralized procurement. By 2023, annual sales fell to 512 million RMB. GSK, holding the commercial rights from Gilead, controlled nearly 73% of the market.
• Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF): An improved version of TDF requiring just one-tenth the dose, TAF gained rapid traction after its 2018 approval, reaching 1.7 billion RMB in 2022. Gilead remains the dominant player with nearly 80% market share.
• Tenofovir Amibufenamide (TMF / Aimtrititide): Developed by Hansoh, TMF is the first domestically developed novel NA and was approved in 2021. Offering improved liver targeting and reduced side effects, TMF achieved 587 million RMB in 2023 sales—an impressive second-year performance.
In summary, while price competition has pressured older NA products like ETV and TDF, newer therapies such as TAF and TMF are capturing market share with improved profiles. Future market expansion is expected to be driven by drugs with novel mechanisms and combination regimens.
Ⅲ、Liver Cancer Drug Market Analysis
3.1 Introduction to Primary Liver Cancer
Primary liver cancer is currently the 4th most common malignant tumor and the 2nd leading cause of cancer death in China, posing a serious threat to the lives and health of the Chinese population. Primary liver cancer originates in the liver tissue and is relatively common in East Asia. It mainly includes three distinct pathological types: Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), and Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma (cHCC-CCA). HCC is the most common primary liver cancer, accounting for 75%~85% of all liver cancer cases.
3.2 Market Performance of Targeted Liver Cancer Drugs
According to Minsent RxSales database statistics, as of December 2024, the globally approved small-molecule targeted drugs for liver cancer include: Sorafenib and Regorafenib (Bayer), Cabozantinib (Exelixis), Apatinib (Hengrui Medicine), Ramucirumab (Eli Lilly), Lenvatinib (Eisai), and Donafenib (Zelgen Biopharmaceuticals).
(1)Lenvatinib
Lenvatinib is an oral multi-kinase inhibitor that selectively inhibits the activity of various kinases, including vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and VEGFR3), fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4), as well as other receptor tyrosine kinases involved in pathogenic angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression, such as platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRα), KIT, and RET.
Developed by Eisai, lenvatinib was approved by the FDA in 2018 for systemic treatment of advanced HCC, marking the first new drug approved for first-line treatment of advanced HCC in over a decade after sorafenib. It was also approved in China the same year.
As a monotherapy, lenvatinib has been approved in Japan, the US, Europe, China, and other regions for the first-line treatment of thyroid cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma, and in Japan for the treatment of thymic carcinoma. The combination therapy of lenvatinib and everolimus has been approved in the US, Europe, and Asia for second-line treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Its combination with the anti-PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab has been approved in multiple regions for first-line treatment of RCC and for endometrial carcinoma following prior systemic therapy.
Minsent RxSales data shows that lenvatinib was first included in the NRDL in 2020, leading to significant sales growth in 2021 with annual sales reaching 1.656 billion RMB. Sales peaked at nearly 2.8 billion RMB in 2022 but showed a downward trend in 2023 and the first half of 2024 due to increased competition.
(2)Donafenib
Donafenib is a novel oral multi-kinase inhibitor. It exerts dual inhibitory, multi-target blocking anti-tumor effects by inhibiting the activity of various tyrosine kinase receptors such as VEGFR and PDGFR to block tumor angiogenesis, and by blocking the serine-threonine kinase (RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK) signaling pathway to directly inhibit tumor cell proliferation.
Donafenib is a deuterated compound of sorafenib, theoretically sharing the same mechanism of action as sorafenib (multi-kinase inhibition). Clinical trial results showed similar median progression-free survival (PFS) between donafenib and sorafenib groups, but the donafenib group demonstrated better safety and tolerability.
Developed by Zelgen Biopharmaceuticals, donafenib was approved by the NMPA in 2021 for first-line treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients who have not received systemic therapy. It was later also approved for radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (RAIR-DTC). After inclusion in the NRDL at the end of 2022, sales grew rapidly in 2023, reaching 426 million RMB for the year, and exceeded 252 million RMB in the first half of 2024.
3.3 Market Performance of Immunotherapy Drugs
(1)1. Multiple PD-(L)1 Combination Regimens Become CSCO First-Line Recommended Therapies
In recent years, PD-(L)1 inhibitors have been increasingly applied in liver cancer treatment. Several domestic PD-(L)1 drugs have been approved for first- and second-line liver cancer therapy, and the CSCO guidelines recommend several PD-(L)1 combination regimens as first-line treatment options. Examples include Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab, Durvalumab + Tremelimumab, and Camrelizumab + Apatinib. These combination regimens have demonstrated significant clinical efficacy in trials, becoming new choices for liver cancer treatment.
Atezolizumab (Tecentriq®, PD-L1) + Bevacizumab (Avastin®, VEGF): Approved by the FDA in May 2020 and by the NMPA in October 2020 for first-line liver cancer treatment. Clinical study results showed the "T+A" regimen achieved a median overall survival (mOS) of 19.2 months, significantly superior to sorafenib's 13.4 months. Bevacizumab is included in the 2022 NRDL, but atezolizumab is not yet included.
Durvalumab (PD-L1) + Tremelimumab (CTLA-4) Dual Immunotherapy: Clinical trial results showed an mOS of 16.4 months, superior to sorafenib's 13.8 months.
Camrelizumab (PD-1) + Apatinib (VEGFR-2 TKI) - Hengrui's "Shuang'ai Combo": Results from the global multicenter Phase III study comparing this combination to sorafenib for advanced unresectable HCC showed an mOS of 22.1 months, superior to sorafenib's 15.2 months.
(2)Domestic PD-(L)1 Market Size Exceeds 21 Billion RMB, Leading Companies Dominate
The overall domestic sales of PD-(L)1 inhibitors exceeded 21 billion RMB, with BeiGene and Innovent Biologics leading the market.
Since the first PD-(L)1 was approved domestically in 2018, 15 PD-(L)1 drugs have been approved by December 2024, with sales surging steadily. Sales grew from 5.7 billion RMB in 2019 to 21.1 billion RMB in 2023. Key drivers include: significant clinical efficacy; broad indications covering various cancers like lung cancer, liver cancer, gastric cancer, and melanoma.
Looking at the competitive landscape of domestic sales in 2023 [only counting PD-(L)1 drugs approved for liver cancer]:
BeiGene's Tislelizumab ranked first with sales of 4.5 billion RMB and a 24.75% market share.
Innovent Biologics' Sintilimab ranked second with sales of 4.0 billion RMB and a 22% share.
Merck's Pembrolizumab ranked third with sales of 3.2 billion RMB (17%). Its strong performance despite not being in the NRDL is attributed to its first-mover advantage, widely approved indications, and Merck's strong sales capabilities.
3.4 Liver Cancer Drug Market Trend Analysis
(1)Perioperative Therapy and Combination Therapy R&D
Postoperative recurrence rates for liver cancer are high, and several perioperative drug therapies are in Phase III clinical trials.
The low surgical resection rate and extremely high postoperative recurrence rate are major challenges in the clinical treatment of early-stage liver cancer, creating an urgent need for effective perioperative regimens. Several Phase III perioperative studies are currently underway, including:
Junshi Biosciences' Toripalimab: Its NDA for combination with bevacizumab as first-line treatment for unresectable or metastatic HCC was accepted by the CDE in July 2024.
Akeso's Cadonilimab (PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody): Approved for second-line cervical cancer and first-line gastric cancer indications; currently in Phase III trials for first-line HCC and HCC perioperative therapy.
Data Insight: After entering the NRDL, sorafenib sales volume (defined as the number of minimum packaging units sold) increased significantly, with 2018 sales being about 3 times higher than in 2017. After the NRDL term expired in 2019, sorafenib was renegotiated for a price reduction and re-included in the NRDL, leading to record-high sales volume in 2020 (4,373,846 tablets). Sales volume fell in 2021, decreasing by 16.6% compared to the 2020 peak.
(2)Internationalization and Differentiation as Key Strategies for Breakthrough
Hengrui's "Shuang'ai Combo" (Camrelizumab + Apatinib) is nearing approval in the US.
Zelgen Biopharma's Donafenib has initiated an international multicenter clinical trial.
Local pharmaceutical companies are entering the global market leveraging "differentiated efficacy + cost advantages."
Drugs like Lenvatinib and Donafenib are extending their indications to thyroid cancer, renal cancer, etc., to prolong their product lifecycles.
(3)Intensifying Market Competition and Future Outlook
Continued Centralized Procurement: National volume-based procurement policies significantly impact drug prices, compressing profit margins for some drugs. Centralized procurement will continue, intensifying competition in the generic drug market.
Innovative Drug R&D: The continuous emergence of innovative drugs challenges existing therapies. Future market competition will be fiercer, with proprietary innovative drugs holding a competitive advantage.
Combination Therapies Become Mainstream: Multi-target, multi-mechanism combination therapies, which improve treatment efficacy, will become the primary development direction in the future.
In conclusion, the liver cancer drug market is fiercely competitive yet full of opportunities. Targeted drugs and immunotherapy drugs together form a complex and dynamic competitive landscape. Current market trends show that combination therapies, with their superior efficacy, are gradually becoming the mainstream, driving continuous market expansion. Simultaneously, research into perioperative therapies addressing the challenges of liver cancer surgery is advancing steadily, showing promising development prospects. Looking ahead, with the rapid advancement of technology and deeper medical research, more innovative drugs and treatment regimens are expected to emerge, further enhancing the standard of liver cancer care and bringing more hope to patients.
Ⅳ、Analysis of Novel Hepatitis B Drug R&D
4.1 Overview of Innovative Mechanisms in New Drug Development
Unlike traditional nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) and interferons, current globally investigational hepatitis B (HBV) drugs involve various mechanisms, including: capsid assembly modulators (CAMs), entry inhibitors, siRNA/ASO gene silencing, gene therapies, etc. These cover diverse drug types such as small molecules, antibodies, fusion proteins, immunoglobulins, siRNA/ASO, and gene editing therapies, presenting a multi-mechanism, multi-target, and diversified R&D landscape. Based on their mechanism of action, novel HBV drugs can be broadly categorized into two classes:
Direct Antiviral Action: Inhibits HBV replication and infection by directly targeting the virus and its components. Includes: CAMs, entry inhibitors, siRNA/ASO gene silencing.
Indirect Antiviral Action: Primarily enhances HBV clearance by activating the host immune system. Includes: therapeutic vaccines, immune checkpoint inhibitors, immunoglobulins.
4.2 Landscape of Investigational Drugs